Introduction
The role of family in Nigerian culture is a cornerstone of society, shaping individuals and communities through strong bonds, traditions, and shared values. Family in Nigeria is not just a social unit but a powerful institution that influences social behavior, economic activities, and cultural identity. This article explores the multifaceted role of family in Nigerian culture, its structure, values, challenges, and evolving dynamics, using simple language and real-life case studies.
In Nigerian culture, the family is the primary unit of social organization. It extends beyond the nuclear family to include extended relatives, creating a large support network. The role of family in Nigerian culture is to provide emotional support, social identity, economic assistance, and cultural continuity.
Family Structure in Nigerian Culture
- Nuclear Family: Consists of parents and their children.
- Extended Family: Includes grandparents, uncles, aunts, cousins, and sometimes close family friends.
- Polygamous Families: Common in some Nigerian ethnic groups, where a man may have multiple wives and children.
| Family Type | Description | Common in Ethnic Groups |
|---|---|---|
| Nuclear Family | Parents and children | Urban areas, modern families |
| Extended Family | Includes wider relatives | Yoruba, Igbo, Hausa, and others |
| Polygamous Family | One man, multiple wives and children | Predominantly Hausa and some Yoruba |
The Role of Family in Nigerian Culture: Social and Emotional Support
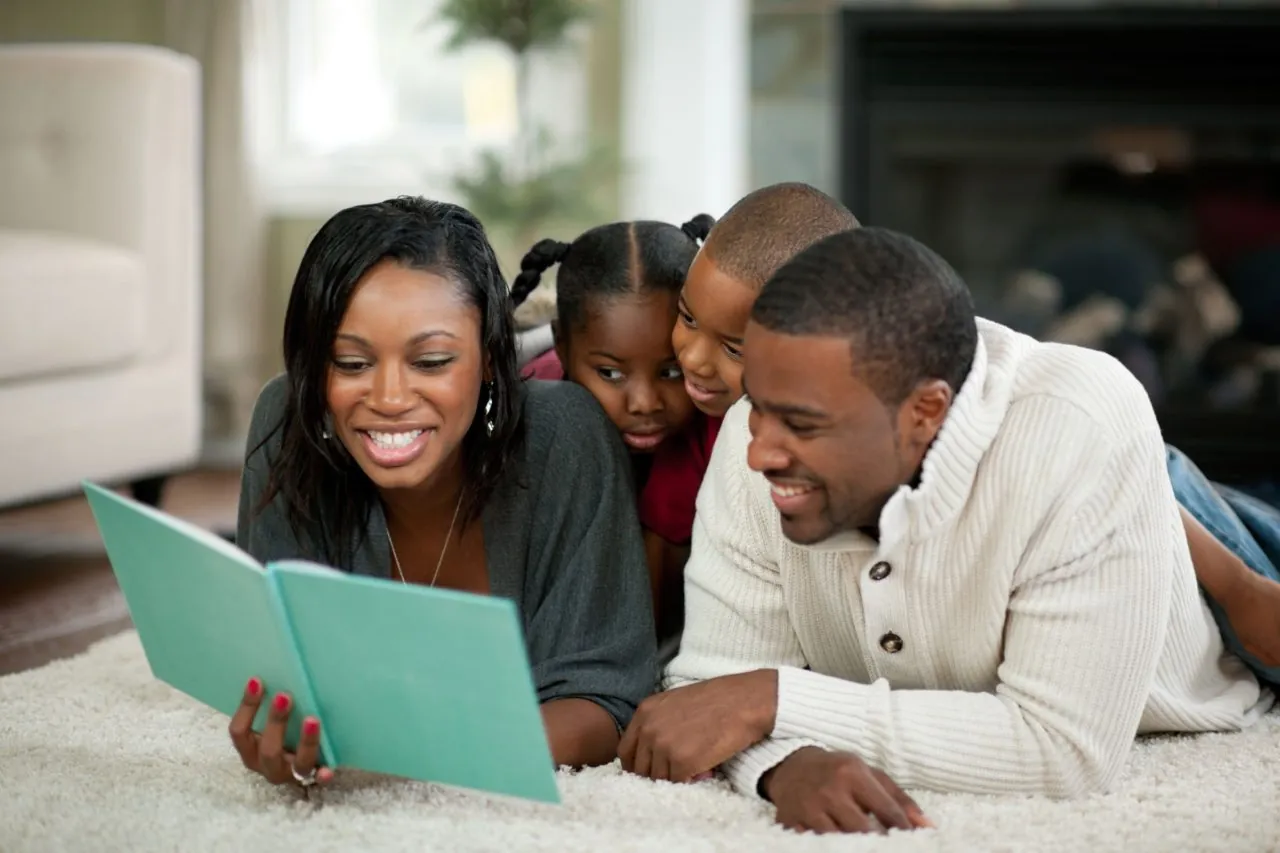

Families in Nigeria are the first source of socialization. From birth, children learn values, norms, and behaviors within the family setting.
Emotional Support and Care
- Parents nurture and guide children through life’s challenges.
- Elders provide wisdom and advice.
- Family members support each other during illness, loss, or hardship.
Socialization and Education
- Families teach language, customs, and traditions.
- Children learn respect for elders and communal living.
- Family involvement in education is strong, often funding schooling and encouraging academic success.
Economic Role of Family in Nigerian Culture
The family acts as an economic unit in Nigerian society.
- Pooling Resources: Family members contribute financially to support each other.
- Inheritance and Property: Family wealth and land are passed down through generations.
- Family Businesses: Many Nigerian businesses are family-owned and operated.
- Support Networks: Families help members find jobs, start businesses, and secure loans.
The Role of Family in Nigerian Culture: Marriage and Childbearing

Marriage is a vital institution in Nigerian families, often involving extended family participation.
Marriage Customs and Family
- Families arrange or approve marriages, sometimes involving bride price negotiations.
- Weddings are family affairs, reinforcing social ties and alliances.
- Polygamy is practiced in some cultures, affecting family dynamics.
Childbearing and Family Expectations
- Children are highly valued as a source of joy and continuity.
- Large families are common, especially in rural areas.
- Parents invest heavily in child upbringing, education, and social status.
Case Study 1: The Yoruba Family System and Its Role
The Yoruba people emphasize the extended family system, where uncles, aunts, and cousins play active roles in child-rearing and decision-making.
- Family Meetings: Regular gatherings to discuss issues and make collective decisions.
- Respect for Elders: Elders are highly respected and consulted.
- Aso-Ebi Tradition: Families wear matching clothes during celebrations to show unity.
Case Study 2: The Igbo Family and Communal Living
Among the Igbo, the family is a vital support system, especially in rural communities.
- Umunna: A kinship group responsible for social welfare and conflict resolution.
- Extended Family Homes: Multiple generations often live together.
- Communal Farming: Family members work together on farms to support the household.
Challenges Affecting the Role of Family in Nigerian Culture

Despite its strength, the Nigerian family faces challenges.
- Urbanization: Migration to cities can weaken extended family ties.
- Modernization: Western values sometimes conflict with traditional family roles.
- Economic Hardships: Poverty affects family cohesion and support.
- Changing Gender Roles: Women’s increasing independence shifts traditional family dynamics.
Respect and Authority
Respect for elders and authority is a key value.
- Children are taught to obey and honor parents and elders.
- Elders have authority in family decisions and conflict resolution.
- Family elders often mediate disputes and maintain order.
Religion and Spirituality
Family plays a central role in religious practices.
- Families teach religious beliefs and rituals to children.
- Religious ceremonies often involve the entire family.
- Spiritual guidance is sought from family elders or religious leaders.
Festivals and Celebrations
Families come together to celebrate important events.
- Birthdays, weddings, naming ceremonies, and funerals are family-centered.
- Traditional festivals reinforce family and community bonds.
- Food, music, dance, and attire reflect family heritage.
Key Roles of Family in Nigerian Culture
| Role | Description | Impact on Society |
|---|---|---|
| Socialization | Teaching values, norms, and language | Cultural continuity and identity |
| Economic Support | Financial pooling, family businesses | Economic stability and growth |
| Emotional Support | Care during hardships and celebrations | Mental health and social cohesion |
| Authority & Respect | Elders’ guidance and decision-making | Social order and conflict resolution |
| Religious Guidance | Teaching faith and rituals | Spiritual well-being and community unity |
| Celebration & Festivals | Family gatherings for important life events | Strengthening family and cultural bonds |
The Future of the Role of Family in Nigerian Culture
As Nigeria modernizes, the role of family in Nigerian culture adapts but remains vital.
- Technology connects family members across distances.
- New family forms emerge, including single-parent and blended families.
- Efforts to preserve traditional family values continue alongside modernization.
Gender Roles and Responsibilities

In Nigerian families, the role of family in Nigerian culture strongly defines gender roles that influence daily life and family dynamics. Traditionally, men are seen as providers and heads of households, responsible for financial support, decision-making, and protecting the family. Women, on the other hand, often take on caretaking responsibilities, managing child-rearing and household duties, while also maintaining family harmony and social networks. However, the role of family in Nigerian culture is evolving as modernization and education empower many Nigerian women to balance traditional roles with careers and leadership positions, reshaping family structures.
Parenting Styles and Child Discipline
The role of family in Nigerian culture includes collective parenting, where beyond biological parents, extended family members like grandparents, aunts, and uncles actively participate in raising children. Discipline within Nigerian families emphasizes respect, obedience, and responsibility. Traditional methods, including verbal correction and guidance, are common, though attitudes toward corporal punishment are gradually changing. The role of family in Nigerian culture also involves instilling moral teachings, religion, and social norms from an early age.
Elderly Care and Respect
A vital aspect of the role of family in Nigerian culture is caring for the elderly. Many elderly parents live with their children or extended family members, receiving both emotional and financial support. Elders are highly respected and often consulted for advice and family decisions, reflecting the deep-rooted cultural value of honoring one’s ancestors and seniors.
Impact of Migration and Urbanization
The role of family in Nigerian culture faces significant changes due to migration and urbanization. Rural-to-urban migration has led many young Nigerians to cities in search of work, resulting in smaller nuclear families and weakening extended family ties. Additionally, transnational families formed by migration abroad maintain connections through remittances and technology, but physical separation challenges traditional family roles.
Family Conflict and Resolution Mechanisms
Conflicts within families are natural, yet the role of family in Nigerian culture emphasizes reconciliation and harmony. Common sources of conflict include inheritance disputes, marital issues, and generational differences. Elders and family heads often mediate disputes, using family meetings, apologies, and traditional rituals to restore peace.
Influence on Social Status and Identity
Family heritage plays a crucial part in the role of family in Nigerian culture, influencing social status and personal identity. Lineage and ancestry confer respect and social standing, while family names reflect ethnic identity and history. Social networks built through family connections often provide access to economic opportunities and social mobility.
Celebrations and Rituals that Strengthen Family Bonds
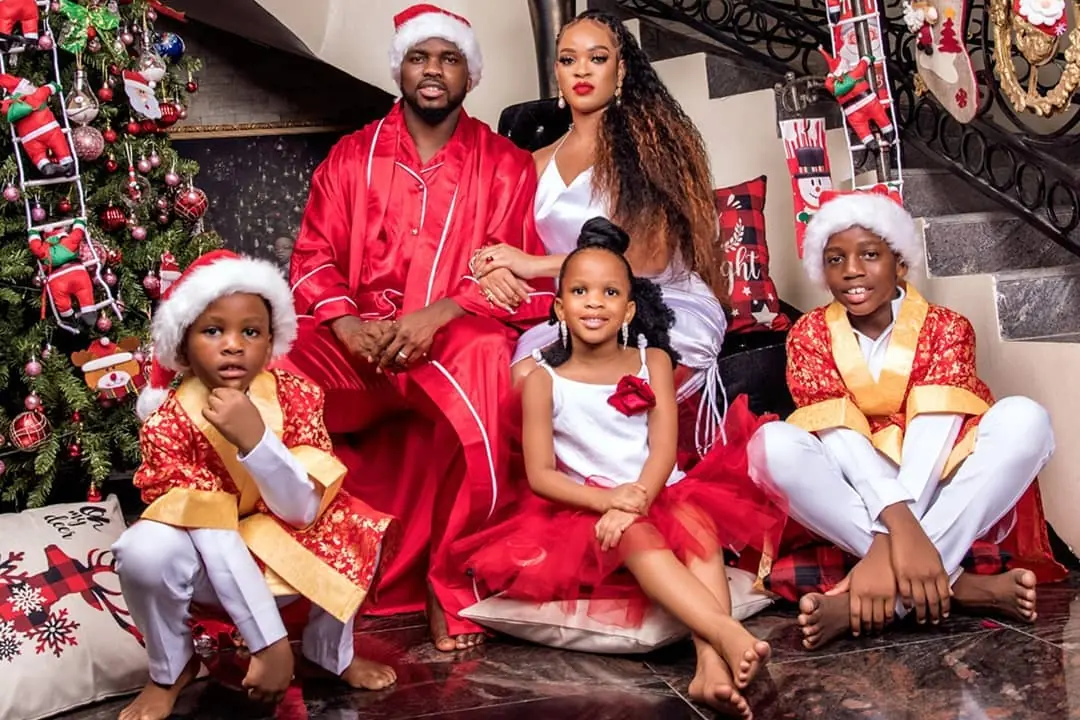

The role of family in Nigerian culture is vividly expressed through celebrations and rituals. Naming ceremonies, marriage events, funerals, and festivals bring families together, reinforcing unity and cultural identity. These occasions are marked by shared meals, music, dance, and traditional attire, showcasing the strength of family ties.
Impact of Technology on Family Communication
Technology has transformed the role of family in Nigerian culture by reshaping communication. Mobile phones and social media enable family members to maintain constant contact despite geographic distances. Virtual gatherings through video calls have become especially important for diaspora families, though some worry that technology may reduce face-to-face interactions and traditional practices.
Influence on Mental Health and Well-being
The role of family in Nigerian culture is critical in supporting mental health and emotional well-being. Families provide primary emotional support during times of stress or illness. However, traditional beliefs sometimes stigmatize mental health issues, influencing care-seeking behavior. Family and community rituals often serve therapeutic functions, fostering psychological healing and resilience.
Impact on Gender Equality and Women’s Empowerment
While the role of family in Nigerian culture traditionally assigns women domestic responsibilities, families can also be platforms for women’s empowerment. Support for women’s education and entrepreneurship within families fosters empowerment, though patriarchal structures may limit autonomy. Increasing education and advocacy are gradually shifting family attitudes toward greater gender equality.
Influence on Political Socialization and Civic Engagement
Families play a significant role in political socialization, a vital aspect of the role of family in Nigerian culture. Political discussions within families educate members about civic duties and national issues. Family influence often shapes voting behavior and political affiliations, while instilling values of community service and patriotism.
Impact of Education on Family Roles and Expectations
Education has transformed many aspects of the role of family in Nigerian culture. Educated parents may adopt more egalitarian parenting styles and encourage diverse career paths for their children. Education is widely viewed as a pathway to social mobility, with families investing heavily in schooling to improve future prospects.
Family Rituals and Their Symbolic Meanings
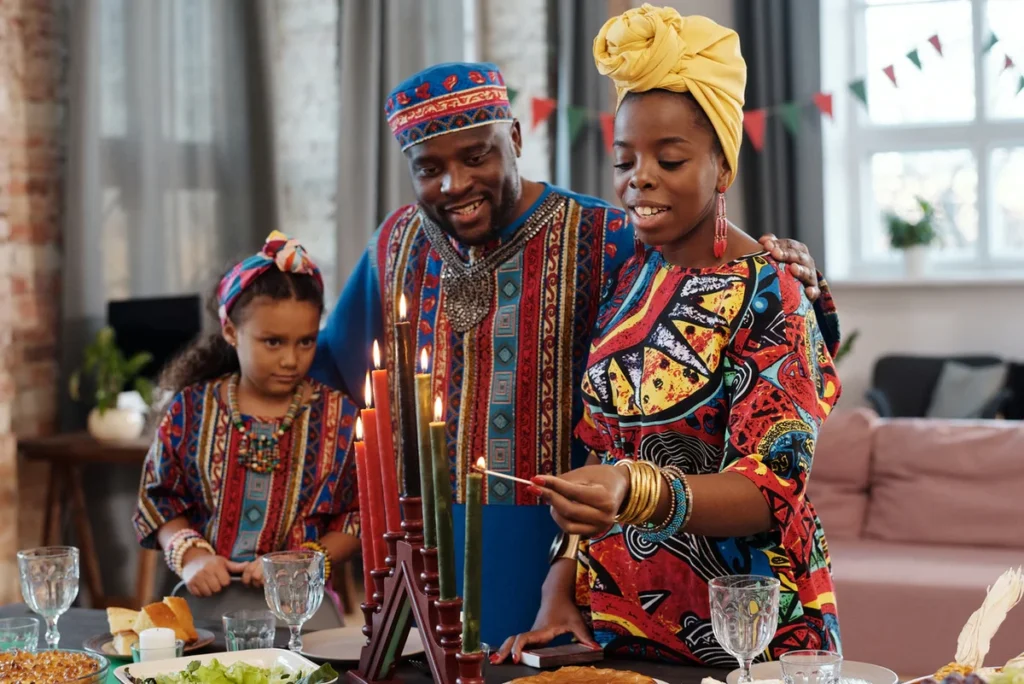

Family rituals are central to the role of family in Nigerian culture, carrying deep symbolic meanings. Naming ceremonies symbolize identity and community belonging; marriage rites represent alliance building and continuity; funerary rites honor ancestors and affirm lineage; harvest and festival rituals celebrate prosperity and gratitude.
Family and Social Change
Families both preserve traditions and adapt to social change, reflecting the dynamic role of family in Nigerian culture. While families act as guardians of cultural heritage, many incorporate modern values alongside traditional ones. Intergenerational differences may cause tension but also promote growth and adaptation.
Influence of Religion on Family Life
Religion profoundly shapes the role of family in Nigerian culture. Religious teachings guide family ethics, marriage, and child-rearing practices. Interfaith families navigate religious diversity, while participation in religious festivals strengthens family unity and spiritual bonds.
Family and Social Networks
Families form the backbone of social networks, a fundamental aspect of the role of family in Nigerian culture. Kinship networks provide social capital and mutual aid. Marriage alliances expand family influence and social ties, while families often hold leadership roles in local governance and community affairs.
Legal and Policy Frameworks Affecting Families
Government laws and policies impact the role of family in Nigerian culture. Marriage laws regulate family formation and rights; child protection laws influence parenting and welfare; social welfare policies address family support systems and poverty alleviation, shaping family life in modern Nigeria.
Parenting Styles and Child Discipline
Parenting in Nigerian culture is guided by communal values and respect for authority.
- Collective Parenting: Beyond biological parents, extended family members like grandparents, aunts, and uncles participate in raising children.
- Discipline: Emphasis on respect, obedience, and responsibility. Traditional methods include verbal correction, guidance, and sometimes corporal punishment, though attitudes are evolving.
- Education and Moral Teaching: Families instill cultural values, religion, and social norms from an early age.
Elderly Care and Respect
Taking care of elders is a sacred duty in Nigerian families.
- Living Arrangements: Many elderly parents live with their children or extended family members.
- Respect and Authority: Elders are highly respected, often consulted for advice and family decisions.
- Social Security: In the absence of formal pension systems, families provide financial and emotional support to aging members.
Impact of Migration and Urbanization
Migration and urbanization have transformed family structures and roles in Nigeria.
- Rural to Urban Migration: Many young Nigerians move to cities for work, leading to nuclear families and weakening extended family ties.
- Transnational Families: Migration abroad creates families separated by distance but connected through remittances and communication technologies.
- Challenges: Urban living can lead to reduced family support networks and increased individualism.
Family Conflict and Resolution Mechanisms
Conflicts are inevitable in families, but Nigerian culture emphasizes reconciliation.
- Sources of Conflict: Can include inheritance disputes, marital issues, and generational differences.
- Mediation: Elders, family heads, and sometimes community leaders act as mediators.
- Traditional Practices: Family meetings, apologies, and rituals are used to restore harmony.
Influence on Education and Career Choices

Families play a significant role in shaping educational and career paths.
- Parental Expectations: Families often guide children towards careers in medicine, law, engineering, or business.
- Financial Support: Families invest in education and training, sometimes pooling resources.
- Pressure and Support: While some children feel pressure to meet family expectations, many receive strong encouragement and mentoring.
Influence on Social Status and Identity
Family background strongly influences social standing and personal identity.
- Lineage and Heritage: Family history and ancestry confer respect and status.
- Family Names: Names often reflect ethnic identity, history, and values.
- Social Networks: Family connections provide access to social and economic opportunities.
Family Planning and Population Trends
Family size and planning are influenced by cultural values and economic factors.
- Preference for Large Families: Traditionally, large families are valued for social and economic reasons.
- Modern Trends: Urbanization and education have led to smaller family sizes in some areas.
- Family Planning: Increasing awareness and use of family planning methods coexist with traditional beliefs.
Celebrations and Rituals that Strengthen Family Bonds
Special occasions reinforce family unity and cultural identity.
- Naming Ceremonies: Celebrating the birth and naming of a child with family and community.
- Marriage Ceremonies: Family involvement is central, with elaborate rituals and celebrations.
- Funerals: Important for honoring ancestors and bringing the family together.
- Festivals: Cultural festivals often involve families in collective celebrations.
The Impact of Technology on Family Communication
Technology has reshaped how Nigerian families interact.
- Mobile Phones and Social Media: Enable constant communication across distances.
- Virtual Family Gatherings: Video calls help maintain connections, especially for diaspora families.
- Challenges: Some worry technology reduces face-to-face interactions and traditional practices.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: How important is the extended family in Nigerian culture?
A: Extremely important; it provides social, economic, and emotional support beyond the nuclear family.
Q: Does polygamy still exist in Nigerian families?
A: Yes, especially in some ethnic groups and rural areas, though it is less common in urban centers.
Q: How do Nigerian families handle conflicts?
A: Elders and family heads usually mediate disputes to maintain harmony.
Q: What role do Nigerian families play in education?
A: Families strongly support education, often funding and encouraging children’s schooling.
Conclusion
The role of family in Nigerian culture is a powerful force that shapes individuals and society. It fosters social cohesion, economic support, cultural identity, and spiritual growth. Despite modern challenges, Nigerian families continue to adapt and thrive, preserving their rich heritage and values for future generations.