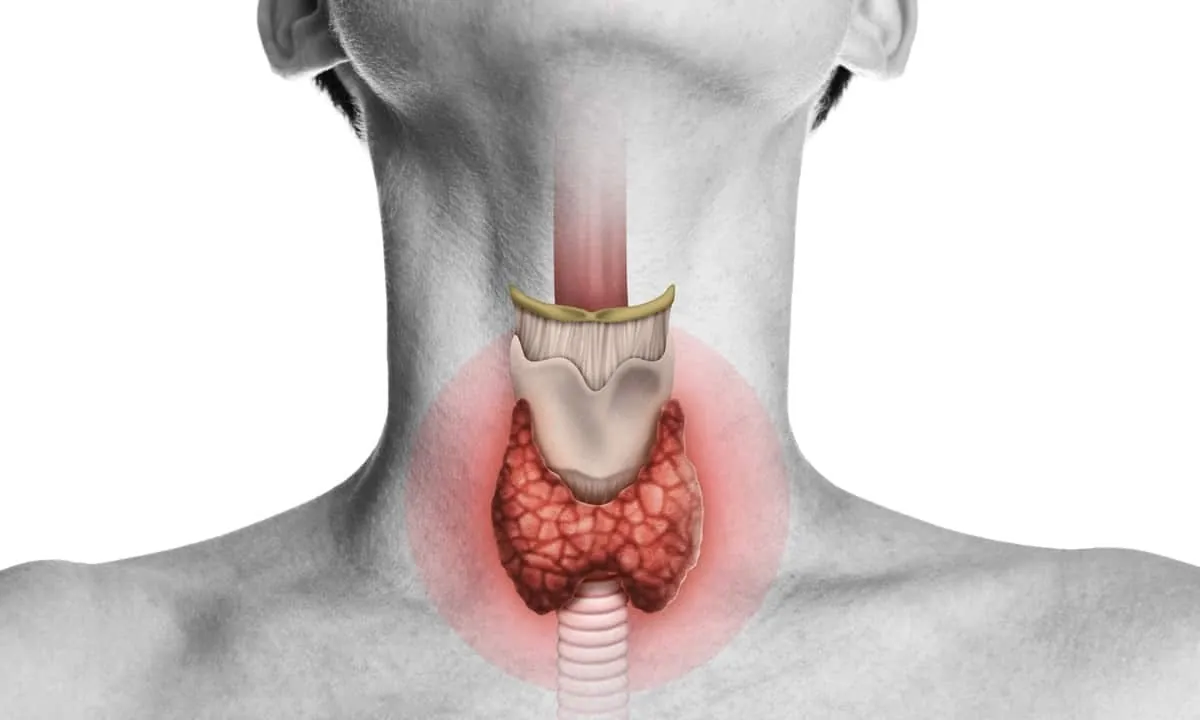
If you’re wondering how to balance thyroid hormones hyperthyroidism, you’re seeking practical ways to manage an overactive thyroid and reduce its impact on your health. Hyperthyroidism occurs when the thyroid gland produces too much of the thyroid hormones (T3 and T4), leading to symptoms like rapid heartbeat, weight loss, anxiety, and heat intolerance. Properly balancing these hormones requires a combination of medical strategies, lifestyle changes, and occasionally natural support.
This comprehensive guide explores effective treatments, dietary and lifestyle tips, and actionable advice for anyone wanting to support optimal thyroid hormone balance during hyperthyroidism.
What Is Hyperthyroidism and Why Does Hormone Balance Matter?
The thyroid gland is a butterfly-shaped organ in your neck that regulates your metabolism by producing thyroid hormones. When it produces excessive hormones:
- Your metabolism speeds up excessively.
- Symptoms range from nervousness and sweating to heart problems.
- Long-term imbalance can seriously affect your heart, bones, and overall health.
Balancing thyroid hormones helps stabilize your body’s systems and restores normal functioning.
How to Balance Thyroid Hormones Hyperthyroidism: Medical Treatments
1. Anti-Thyroid Medications
Thionamides like methimazole (Tapazole) and propylthiouracil (PTU) reduce the thyroid gland’s hormone production.
- These drugs help your hormone levels return to normal over weeks to months.
- Methimazole is usually preferred due to fewer side effects.
- PTU is sometimes used during pregnancy or when methimazole isn’t tolerated.
- Side effects may include mild nausea, rash, or rarely, serious blood-related conditions requiring immediate medical attention.
2. Beta-Blockers to Manage Symptoms
Beta blockers such as propranolol are prescribed to ease hyperthyroid symptoms:
- They do not reduce hormone levels but help control rapid heartbeat, tremors, and anxiety.
- They provide relief until hormone levels are stabilized.
3. Radioactive Iodine Therapy
Radioactive iodine (RAI) treatment involves swallowing a dose of radioactive iodine that is selectively absorbed by the thyroid gland, destroying overactive thyroid cells.
- It’s often very effective but commonly results in hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid).
- Life-long thyroid hormone replacement therapy is typically required afterward.
- Not recommended for pregnant or breastfeeding women.
4. Surgery (Thyroidectomy)
Surgical removal of part or all of the thyroid gland may be recommended if:
- You have large goiters causing symptoms.
- Radioactive iodine or medications are contraindicated or ineffective.
- You prefer a definitive treatment.
Surgery also usually requires subsequent hormone replacement.
Natural and Lifestyle Strategies to Support Thyroid Hormone Balance
While medical treatment is essential, natural strategies can support your body during hyperthyroidism and complement conventional therapy.
1. Mind Your Diet: Avoid Excess Iodine
Since iodine fuels thyroid hormone production, controlling iodine intake may help reduce hormone excess:
- Avoid iodine-rich foods such as seaweed, iodized salt, dairy products, and some seafood.
- A low-iodine diet is sometimes recommended before radioactive iodine therapy.
- Eat balanced meals with plenty of vegetables, fruits, whole grains, and lean proteins.
2. Focus on Anti-Inflammatory and Nutrient-Rich Foods
Inflammation can worsen thyroid issues, so include foods with natural anti-inflammatory properties:
- Berries, turmeric, leafy greens, and ginger can help soothe inflammation.
- Selenium-rich foods (Brazil nuts, sunflower seeds) support thyroid enzyme function.
3. Manage Stress Effectively
Stress worsens hormonal imbalances and triggers symptom flares.
- Practice relaxation techniques like deep breathing, meditation, or yoga daily.
- Ensure adequate and high-quality sleep to regulate hormone production.
4. Avoid Stimulants That Aggravate Symptoms
- Limit or avoid caffeine, nicotine, and energy drinks, which can worsen tremors and anxiety.
- Alcohol can also disrupt endocrine balance and should be consumed cautiously.
5. Gentle Regular Exercise
Moderate exercise helps alleviate anxiety, improves cardiovascular health, and boosts energy without overtaxing your system.
- Focus on gentle activities like walking, swimming, or Pilates.
- Avoid intense workouts during active hyperthyroid symptoms.
6. Consider Supplements (With Doctor’s Approval)
- Selenium supplements may support thyroid function but must be taken under medical supervision to avoid toxicity.
- Vitamin D and magnesium deficiencies are common in thyroid disorders and can be addressed if tested low.
Practical Tips for Living Well With Hyperthyroidism
Track Your Symptoms and Medication Effects
- Keep a daily journal noting symptoms’ severity, medication doses, and side effects.
- Share this with your healthcare provider for personalized adjustments.
Communicate Regularly With Your Healthcare Team
- Regular blood tests are crucial to monitor thyroid hormone levels.
- Discuss any new symptoms or concerns promptly.
Understand That Balancing Thyroid Hormones Can Take Time
- Symptoms may improve gradually over several weeks or months once treatment begins.
- Patience is key, and adherence to prescribed therapies is essential.
When to Seek Urgent Care

Certain hyperthyroidism complications require immediate attention:
- Signs of thyroid storm including fever, confusion, rapid heart rate, or extreme agitation.
- Symptoms of severe allergic reaction to medications: rash, difficulty breathing, swelling.
- Worsening heart symptoms like chest pain or fainting.
The Role of Gut Health in Balancing Thyroid Hormones in Hyperthyroidism
Emerging research shows a strong connection between gut health and thyroid function, sometimes referred to as the “gut-thyroid axis.” Maintaining a healthy gut can be an important yet often overlooked factor when learning how to balance thyroid hormones hyperthyroidism.
How Gut Health Affects Thyroid Hormones
- Gut Microbiota Influence: Beneficial gut bacteria help convert inactive thyroid hormone (T4) to its active form (T3), crucial for metabolism.
- Leaky Gut and Autoimmunity: Hyperthyroidism is often caused by autoimmune conditions such as Graves’ disease. Increased intestinal permeability (“leaky gut”) can exacerbate autoimmune responses.
- Nutrient Absorption: Gut issues can impair absorption of critical nutrients like selenium, zinc, and vitamin D—which are essential for thyroid hormone synthesis and regulation.
Steps to Improve Gut Health for Thyroid Balance
- Consume Probiotic-Rich Foods: Yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, kimchi, and other fermented foods support diverse and healthy gut flora.
- Prebiotic Foods: Foods rich in inulin and fiber such as garlic, onions, asparagus, and bananas nourish probiotics.
- Limit Processed Foods: Reduce intake of highly processed, sugary, and fried foods which can impair gut flora.
- Manage Stress: Chronic stress disrupts gut barrier integrity, so relaxation techniques indirectly benefit gut-thyroid health.
- Consult With a Healthcare Provider: If you experience digestive symptoms like bloating or irregular bowel movements, get evaluated.
Understanding Thyroid Autoimmunity and Its Impact on Hormone Balance
Hyperthyroidism frequently originates from autoimmune causes — most commonly Graves’ disease — where the immune system mistakenly attacks the thyroid gland.

How Autoimmunity Disrupts Hormone Balance
- Autoimmune antibodies stimulate the thyroid gland to produce excess hormones.
- Chronic inflammation damages thyroid tissue and alters hormone feedback mechanisms.
- Fluctuating hormone levels can cause cyclical symptoms and complicate treatment.
Managing Autoimmune Hyperthyroidism Beyond Medication
- Dietary Considerations: Anti-inflammatory eating patterns such as the Mediterranean diet may reduce autoimmune flare-ups. Avoiding gluten is sometimes recommended if sensitivity is present.
- Stress Reduction: Stress increases inflammatory markers which can trigger autoimmunity.
- Immune-Supportive Supplements: Omega-3 fatty acids and vitamin D show promise in modulating immune response but should be used under professional guidance.
- Regular Monitoring: Autoimmune thyroid conditions require ongoing bloodwork to monitor antibodies and hormone fluctuations.
Environmental and Lifestyle Factors That Influence Thyroid Hormone Balance in Hyperthyroid Patients
Besides diet and medications, certain environmental exposures and lifestyle choices can impact your thyroid’s ability to stay balanced.
Environmental Toxins and Thyroid Disruption
- Heavy metals: Mercury, lead, and cadmium have been linked to thyroid dysfunction.
- Endocrine disruptors: Chemicals such as BPA (found in plastics) and pesticides interfere with hormone receptors.
- Radiation exposure: Can exacerbate thyroid gland issues in vulnerable individuals.
How to Minimize Environmental Impact on the Thyroid
- Use BPA-free containers and reduce plastic usage.
- Choose organic produce when possible to limit pesticide intake.
- Avoid unnecessary exposure to industrial chemicals and heavy metals.
- Filter tap water if contaminants are suspected.
Lifestyle and Daily Habits That Can Support Hormone Balance
- Maintain a consistent sleep schedule — disrupted circadian rhythms affect hormone regulation.
- Avoid overtraining during fitness routines; excessive exercise can stress the body.
- Practice mindfulness or meditation to reduce systemic inflammation.
- Limit alcohol and tobacco use, which impair thyroid health.
The Importance of Personalized Treatment Plans in Balancing Thyroid Hormones

Every person’s thyroid condition is unique, and what works effectively for one patient may not for another. Understanding your own thyroid health profile is critical.
Factors Influencing Personalized Care
- Severity and cause of hyperthyroidism
- Age, gender, and underlying medical conditions
- Response and tolerance to medications
- Lifestyle, diet, and environmental exposures
- Presence or absence of autoimmune antibodies
Working With Healthcare Providers for Tailored Therapy
- Regularly update your endocrinologist or healthcare provider on symptoms and side effects.
- Discuss all supplements and alternative approaches to avoid dangerous interactions.
- Adjust treatments gradually with periodic monitoring.
- Consider second opinions or specialty clinics for complicated cases.
Tracking Progress: Using Biomarkers and Symptom Journals to Balance Thyroid Hormones
Monitoring your progress with actionable data provides insight and motivation.
Essential Biomarkers to Track
- TSH (Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone)
- Free T3 and Free T4 levels
- Thyroid antibody levels (TSI, TPO antibodies) if autoimmune
- Calcium and vitamin D levels (as thyroid conditions can impact bones)
Benefits of Symptom Journals
- Helps identify triggers such as stress, foods, or environmental factors.
- Tracks medication effectiveness and side effects.
- Improves communication with your doctor.
Tip: Use apps or notebooks to log energy levels, sleep quality, mood, weight, and other symptoms daily or weekly.
When Alternative and Complementary Therapies May Help Balance Thyroid Hormones

While evidence-based medicine is primary, some complementary approaches can provide supportive benefits.
Acupuncture
- May help reduce symptoms such as anxiety, insomnia, and fatigue commonly seen with hyperthyroidism.
Herbal Supplements
- Herbs like bugleweed or lemon balm have traditionally been used to help manage hyperthyroid symptoms but require professional supervision.
Mind-Body Practices
- Tai Chi and Qi Gong improve energy flow, reduce stress, and support hormone balance.
Caution: Always inform your healthcare provider before starting any alternative treatment to avoid interference with conventional therapies.
Summary: How to Balance Thyroid Hormones Hyperthyroidism Effectively
Balancing thyroid hormones in hyperthyroidism combines effective medical treatments like antithyroid drugs, beta-blockers, radioactive iodine, or surgery with supportive natural strategies and lifestyle changes. Diet plays a key role—avoiding excess iodine and including anti-inflammatory foods supports healing. Managing stress, monitoring symptoms, and close cooperation with your healthcare provider are vital for optimal outcomes.