Navigating the world of health insurance can often feel like learning a new language, with a dictionary full of confusing terms and complex rules. You hear about subsidies, tax credits, and government programs, but what happens when you don’t qualify for any of that? What if you’re on your own, trying to find coverage that fits your needs and your budget? This is where a crucial question arises for millions of people: what is private health plan without financial assistance? This guide is dedicated to answering that question in full.
This is your straightforward, comprehensive manual for understanding how to secure health coverage when you are paying the full price. We will break down exactly what these plans are, who they are designed for, and how to strategically choose the best one for you and your family. The journey of understanding what is private health plan without financial assistance is about taking control of your healthcare decisions with confidence and clarity, ensuring you have the protection you need, paid for entirely on your own terms.
Defining the Terms: What is Private Health Plan Without Financial Assistance?
To truly grasp the concept, let’s break down the phrase piece by piece. Understanding this definition is the essential first step for anyone exploring this type of coverage. The core of what is private health plan without financial assistance lies in its two main components.
- “Private Health Plan”: This refers to any health insurance policy that is not provided or run by the government (like Medicare or Medicaid in the U.S.). Instead, it is offered by a private, non-governmental company. These are the plans you often see offered by employers or that you can buy directly from the insurance company or through a health insurance marketplace.
- “Without Financial Assistance”: This is the key qualifier. It means that the person purchasing the plan is paying 100% of the monthly premium out of their own pocket. They are not receiving any government-provided subsidies, tax credits, or other forms of cost-sharing reductions that are often available to individuals and families with lower incomes.
So, when we combine them, the answer to what is private health plan without financial assistance is simple: It is a health insurance policy from a private company for which the enrollee pays the full, unsubsidized monthly cost. This is the standard way many individuals, including the self-employed and those with higher incomes, purchase their health coverage.
Who Typically Needs This Type of Coverage?
Understanding the target audience helps to clarify the role and importance of these plans. While every individual’s situation is unique, there are several common groups of people who will find themselves in the market for this specific type of insurance. Knowing if you fall into one of these categories is central to understanding what is private health plan without financial assistance.
- Higher-Income Individuals and Families: In many countries with marketplace-style systems, financial assistance is tied to income levels. Individuals or families who earn above a certain threshold (for example, above 400% of the Federal Poverty Level in the United States) do not qualify for premium tax credits. They must purchase their insurance at full price.
- The Self-Employed and Small Business Owners: Entrepreneurs, freelancers, and small business owners who do not have access to a group plan through a large employer often need to buy their own insurance. Depending on their income, they may be looking for a what is private health plan without financial assistance.
- Early Retirees: Individuals who retire before they are eligible for government-sponsored senior healthcare programs (like Medicare, which typically starts at age 65) need to secure their own coverage for the gap years.
- Employees of Companies That Don’t Offer Health Insurance: While many large companies offer health benefits, many smaller businesses do not. Employees at these companies must find and pay for their own private plans. The quest for what is private health plan without financial assistance is very common for this group.
- Those Seeking More Options: Some individuals who may technically qualify for a subsidized plan might choose a what is private health plan without financial assistance “off-exchange” because it gives them access to a wider variety of plans and networks that may not be available through the government marketplace.

Key Components: Understanding the Costs
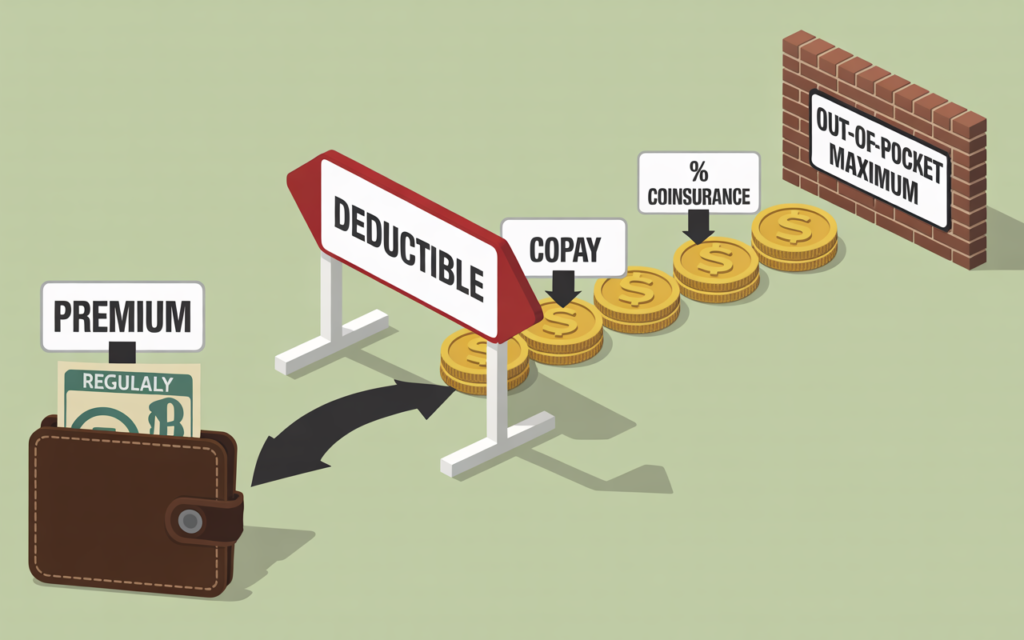
When you are paying the full price, understanding every single cost component is absolutely critical. The monthly premium is just the beginning of the story. A true understanding of what is private health plan without financial assistance requires a deep dive into these key terms.
The Premium
This is the fixed monthly amount you pay to the insurance company to keep your policy active. It’s like a subscription fee. With a what is private health plan without financial assistance, you are responsible for 100% of this amount every month, regardless of whether you use any medical services.
The Deductible
This is the amount of money you must pay out-of-pocket for covered medical services before your insurance plan starts to pay. For example, if your plan has a $3,000 deductible, you pay for the first $3,000 of your covered healthcare costs. After you’ve met your deductible, you move on to paying copayments or coinsurance. Plans with lower monthly premiums often have higher deductibles. This trade-off is a central theme in selecting a what is private health plan without financial assistance.
Copayment (Copay)
This is a fixed amount you pay for a specific covered health care service after you’ve met your deductible. For example, you might have a $40 copay for a doctor’s visit or a $100 copay for an emergency room visit.
Coinsurance
This is your share of the costs of a covered health care service, calculated as a percentage of the allowed amount for the service. For example, if your coinsurance is 20%, and a hospital stay costs $10,000, your insurance company pays 80% ($8,000) and you pay 20% ($2,000), assuming your deductible has already been met. Understanding the interplay between deductibles and coinsurance is vital when considering what is private health plan without financial assistance.
Out-of-Pocket Maximum
This is the absolute most you will have to pay for covered services in a plan year. After you spend this amount on deductibles, copayments, and coinsurance, your health plan pays 100% of the costs of covered benefits. This number is your financial safety net. A lower out-of-pocket maximum provides more protection but usually comes with a higher monthly premium. This is a crucial number to know when you are responsible for the full cost of a what is private health plan without financial assistance.

A Strategic Guide to Choosing Your Plan
Now that you understand the core concepts, it’s time for the practical part: choosing the right plan. This is a significant financial decision, so taking a structured approach is essential. This section is a detailed guide for anyone asking what is private health plan without financial assistance.
Step 1: Assess Your Health and Financial Situation
Before you even look at plans, look at yourself.
- Health Needs: Are you generally healthy, or do you have chronic conditions that require regular doctor visits? Do you take expensive prescription drugs? Are you planning to have a baby or a major surgery in the next year?
- Financial Situation: How much can you comfortably afford for a monthly premium? Critically, how much cash could you access if you had an unexpected medical emergency? This will help you decide between a high-deductible plan (lower premium, more risk) and a low-deductible plan (higher premium, less risk). The answer to what is private health plan without financial assistance is right for you depends on this assessment.
Step 2: Understand the Different Plan “Metal” Tiers
Plans on the marketplace are often categorized into metal tiers: Bronze, Silver, Gold, and Platinum. This is a helpful shorthand for understanding the cost-sharing structure.
- Bronze: Lowest monthly premium, but the highest costs when you need care (high deductible).
- Silver: Moderate monthly premium and moderate costs when you need care.
- Gold: High monthly premium, but low costs when you need care.
- Platinum: Highest monthly premium and the lowest costs when you need care.
Your choice of tier is a personal decision about risk tolerance. The question of what is private health plan without financial assistance you select often comes down to this balance.
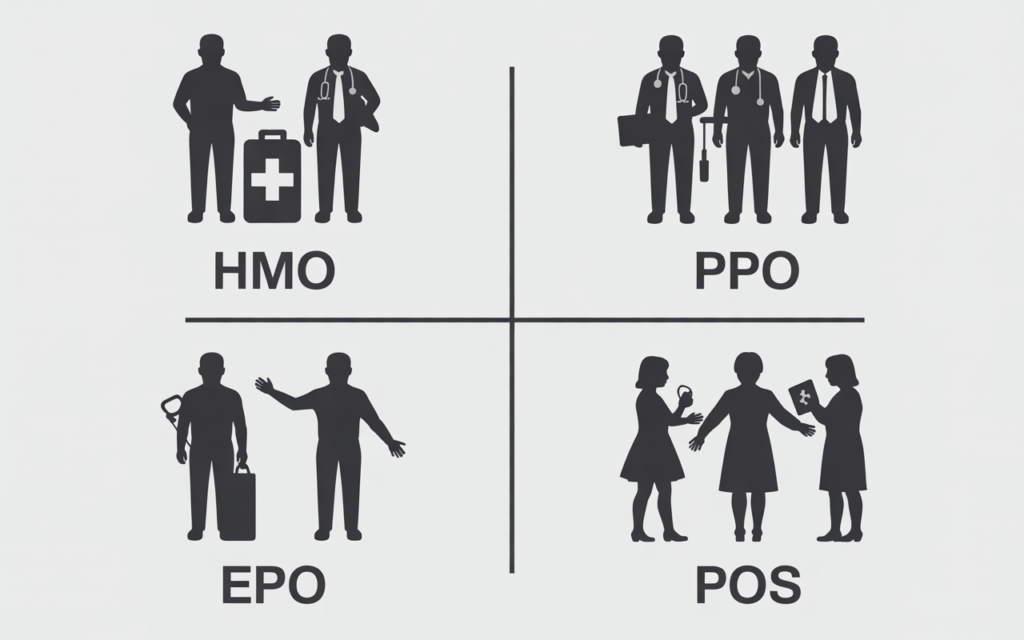
Step 3: Learn the Plan Types (HMO, PPO, EPO, POS)
This is another crucial layer of understanding. The plan type dictates your access to doctors and specialists.
- HMO (Health Maintenance Organization): Usually has lower premiums. You must use doctors, hospitals, and specialists within its network. You will also need to choose a Primary Care Physician (PCP) and get a referral from them to see a specialist.
- PPO (Preferred Provider Organization): Usually has higher premiums. It offers more flexibility. You can see both in-network and out-of-network doctors without a referral, but your costs will be significantly lower if you stay in-network. This flexibility is a key reason people choose a PPO when looking for what is private health plan without financial assistance.
- EPO (Exclusive Provider Organization): A hybrid model. You must use doctors and hospitals within the network (like an HMO), but you usually don’t need a referral to see a specialist.
- POS (Point of Service): Another hybrid. It lets you choose between an HMO or a PPO each time you need care. Like an HMO, it requires you to have a PCP and get referrals.
Step 4: Check the Network Thoroughly
This cannot be overstated. A plan is only as good as the doctors and hospitals it includes. Before you enroll, use the insurance company’s online provider directory to check if your preferred doctors, local hospitals, and pharmacies are in the plan’s network. If you see a specific doctor for a chronic condition, this is a non-negotiable step. When you ask what is private health plan without financial assistance, you must also ask “and who can I see with it?”
Step 5: Compare the Summary of Benefits
Every plan must provide a “Summary of Benefits and Coverage” document. This is a standardized, easy-to-read summary that lets you compare plans side-by-side. Look at the deductibles, out-of-pocket maximums, and copay/coinsurance amounts for the services you are most likely to use. This detailed comparison is the heart of making an informed decision about what is private health plan without financial assistance.

Pros and Cons: A Balanced View
Every type of insurance has its advantages and disadvantages. Being aware of these helps you set realistic expectations.
Pros of a Private Health Plan Without Financial Assistance:
- Greater Choice: You often have access to a wider array of plans, including those “off-exchange” with larger provider networks, than what might be available with subsidized options.
- Autonomy: You have complete control over your plan selection without being limited by subsidy eligibility rules.
- Simplicity: Your financial situation is simpler as you don’t have to worry about reporting income changes to a marketplace to adjust your subsidy amount.
Cons of a Private Health Plan Without Financial Assistance:
- High Cost: This is the most significant drawback. You are responsible for the full premium, which can be a major monthly expense.
- Full Financial Risk: You bear the full brunt of deductibles and other out-of-pocket costs without any cost-sharing reductions.
- Complexity of Choice: The sheer number of available options can be overwhelming, making the decision-making process more difficult.
Final Thoughts: Taking Ownership of Your Health Coverage
The journey to understand what is private health plan without financial assistance is ultimately about empowerment. It’s about recognizing that you have the responsibility—and the power—to make a crucial decision for your financial and physical well-being. It requires diligence, research, and an honest assessment of your own needs.
This is not a decision to be rushed. Take your time, use the tools available to you, and don’t be afraid to ask questions. By carefully considering your budget, your health needs, and your risk tolerance, you can confidently select a plan that provides a strong safety net. While the cost is entirely your own, so is the peace of mind that comes from knowing you have made an informed choice and have secured the protection you and your family deserve. This proactive approach is the best way to manage the reality of what is private health plan without financial assistance.